Everyone working in pharmaceutical industries is familiar with the term QA or Quality Assurance & QC or Quality Control but when we ask them to tell what is the difference between QA & QC or explain QA VS QC then the answer is very short & limited to the following,
- QC controls the quality & QA is involved in the assurance of Quality.
Some may answer like following,
- The department involved in the testing of pharmaceutical products is known as QC & the department involved in in-process checking is known as QA.
The above answers are not wrong but these are short, so in this article we will discuss more than 9 key differences between QA & QC so that you may be able to provide a detailed logical answer to this question.
Definition Of QA
Quality assurance is defined according to ISO 9000.
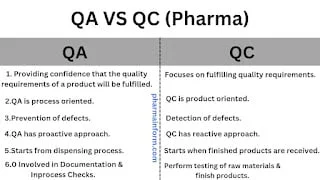
- QA is part of the QMS ( Quality management system) which focuses on providing a confidence that quality requirements of a product will be fulfilled.
Definition Of QC
In ISO 9000, QC is defined as,
- QC is part of the quality management system (QMS) which focuses on fulfilling the quality requirements.

General Understanding Of QA
Quality assurance is the department in pharmaceutical industries which is responsible for assuring the quantity of all products by defining proper written procedures & in-process controls.
General Understanding Of QC
Quality control is the department in pharmaceutical industries which is responsible for controlling the quality of all the incoming raw materials, packaging materials & outgoing finished products by performing testing defined by regulatory bodies.
Orientation Of QA
The quality assurance department is process oriented.
Orientation Of QC
Quality control is product oriented.
Goal Of Quality Assurance
The ultimate goal of the QA department is to prevent any defect during dispensing, manufacturing, printing, and packaging.
Goal Of Quality Control
The ultimate goal of the quality control department is to detect any defect in the raw materials, package materials or finished products.
Approach Of QA
Quality assurance has a proactive approach.
Approach Of QC
Quality control has a reactive type approach
Division Of QA
QA may have the following divisions
- IPQA
- IPQC
- Documentation
Division Of QC
QC may have the following divisions
- Raw Materials Testing
- Packaging Materials Testing
- Finished products Teasing
When To Start (QA)
The responsibilities of the QA department start from the dispensing process till its dispatch.
When To Start (QC)
The responsibilities of the QC department start when finished products are sampled & provided for testing.
For Incoming Materials
The responsibilities of the QC department start when raw materials or packaging materials arrive.
Audit Authority (QA)
The QA department has the power to audit other departments.
Audit Authority (QC)
The QC department has no power to audit other departments.
Complaints Handling (QA)
Customer complaints are investigated & directly handled by the QA department.
Complaints Handling (QC)
Quality control is not directly involved in handling customer complaints.
Examples
Quality Assurance
- For the assurance of product quality, the SOPs, SCPs, and work instructions are prepared by the Quality Assurance department & are implemented.
- In-process checks are performed by the quality assurance department to ensure that the running product is defect free & meets the specifications.
Examples
Quality Control
-
Testing performed for all excipients, active pharmaceutical ingredients & packaging materials before use.
- Testing performed for all finished products before release to dispatch.